What is optical components metallization ?
It refers to the deposition of metal layer(s) on an optical component. (Gold, ITO, Aluminum, Silver, other metals..)
Everything you need to know about optical elements metallization.
Why doing a metallization ?
- Possibility of heating components (for example for defrost them)
- Electro magnetic shielding (Faraday cage principle)
- Support for brasing / welding. Components assembly, hermetic isolation of the component etc.
- Mirror effect, light reflection.
How the metal deposition is carried out ?
Metallization is usually done in a vacuum coating device. It needs custom coating jigs for positioning and shape making of the metallization pattern. Coating is made by batch of several tenth or hundreds of parts, according to the part and the device dimensions.
Which are the different available metallizations ?
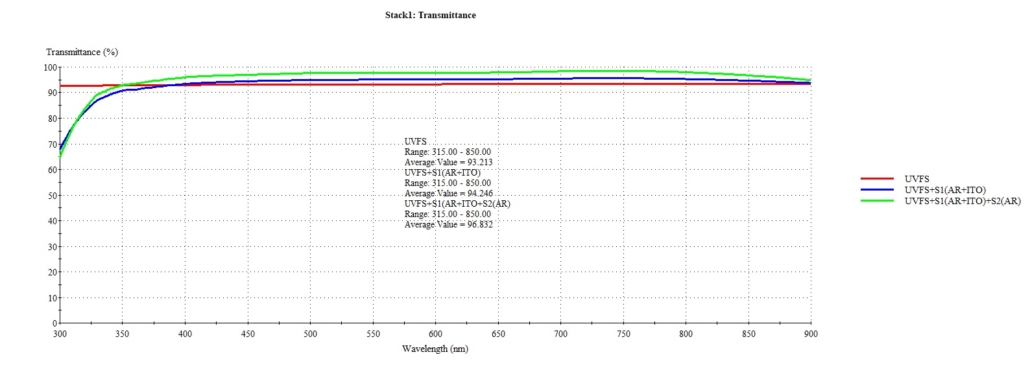
Optical areas treatments : gold, ITO (Indium Tin Oxyde), metallic micro mesh (Cu, Ni) for anti-glare treatments used for protection devices interfaces from sun light.
Around optical areas on the edge of components, for CrNiAu, TiNiAu, TiPtAu etc. mostly for weldability.
It is possible to add AR (anti-reflection) treatment on the metallized components.
Metallization is also used for reflective devices (mirrors) with aluminum, silver or other metal layers according to working wavelengths.
What are the specifications of optical metalisations ?
- Good binding ASTM D2259.83 B
- non ferrous metals, so low oxydation risk. Salt spray test following MIL-C-48497 4.5.5.2
- Thermal resistance : MIL-C-48497, 4.5.4.1
- Solderability : MIL-STD-883
- Custom resistivity (from some ohms to several hundreds ohms for ITO)
Metalization treatments common usages.
- Aerospace / Defense
- Communication / optical fibers
- External used equipment displays
- IR detection
- Bio Medical
- Automotive
- Electromagntic shielding
- Component heating