Our sapphire parts manufacturing solutions
Sapphire optical parts are currently widely used in the industry for it’s very high hardness and good optical transmission from the UV to the IR. Windows are used from watch covers to laser protections, sapphire domes are commun in rockets heads. Lenses and aspherical lenses while expensive as the material is hard to work, may be interesting for demanding applications. Finally SINOPTIX also provides sapphire tubes used in laboratory research centers and industrial applications.
Sapphire windows can be coated with AR treatment and/or metalization that enable welding and/or electric connection to the windows.
Particularities of the material
Glass Sapphire crystal or crystalline corundum, is unlike the gemstone which he get it name from, artificially produce. French chemist Auguste Verneuil is the creator of synthetic sapphire that he produced for the first time in 1902.
The sapphire is usually produced by crystallizing aluminum oxide powder (Al2O3) at high temperature and pressure. There is different development process sapphire crystals of which the most used are the ISM (polycrystalline), KY HEM and EFG CZ (Monocrystalline).
Key Benefits of Sapphire are:
- A very good transmission in the UV – NIR
- Incredibly, tougher What Other Optical glasses (Thermal shock, chemical, mechanical)
- Highly resistant to scratches and abrasion (9 on the Mohs hardness scale, just below the diamond)
- Very high melting temperature
However its high hardness makes it hard for machining, especially complex shapes.
Its transparency and its exceptional hardness make it a coveted glass pour the following applications:
- Watches: watch glass (ONLY scratched by diamond)
- Scanner Glass: Often prone to scratches
- Windows Phone: Apple use pay Fingerprint readers, the Cameras and SOME watches.
- Windows to Resist high temperatures or pressure: laser applications
Sapphire specifications
Below is summary table of optical grade single crystal sapphire specifications:
| characteristicS | Data |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | Al2O3 purity at >99,99% |
| Orientation | random, C-axis, A-plane, R-plane and M-plane |
| Aspect | colorless transparent |
| Melting point | 2030°C (3686 °F) |
| maximum operating temperature | 1900°C |
| thermal conductivity | 41.9 (W/m°K) |
| thermal expansion 20-1000°C | Parallel to axis C: 9.03×10-6 °C Perpendicular to axis C: 8.31×10-6 °C 60° to axis C: 8.4×10-6 °C |
| Tensile Strength | 400 MPa (8500 PSI) |
| Flexural Strength | 1900 MPa (13500 PSI) |
| Specific Gravity | 3.95 – 4.03 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.25-0.30 |
| optical transmission | 200 to 5500 nm |
| refractive index | 1.7122 |
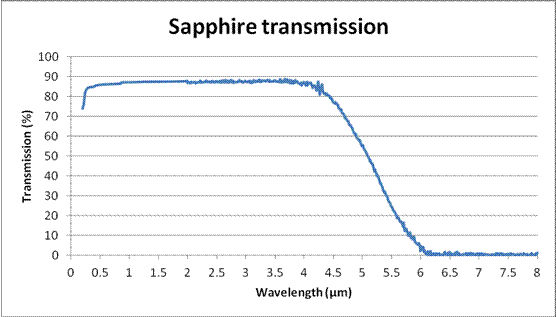
Sapphire transmission
Sapphire is a good optical materials, with Ultraviolet transmission starting as low at 180nm and transmitting in average at 88% in the visible to the near infrared (NIR).
See below the transmission curve of a sapphire window, transmission can be enhanced with Anti-reflect coatings.
Optical components manufacturing
Sapphire is grown as a crystal in industrial laboratories. After crystal growth, the substrate is in a form of a boule that further processing will cut into blanks ready for further precision manufacturing.
During the manufacturing the orientation of the crystal can be checked by X-ray crystal orientation equipment and therefore optical components can be manufactured in a certain direction relative to crystal orientation.
Cutting, centering, chamfreining and polishing are the final production stage of the components. Maximum achievable flatness is Lambda/20.
The maximum dimensions of sapphire parts that we offer is diameter 650mm or 700mm long for rectangular windows. Dimension tolerances can reach +/-0.01mm and roughness less than 0.2nm after polishing.
ASPHERICAL LENS
For very demanding application both in terms of mechanical resistance and optical quality we are helping companies manufacture aspherical lenses in sapphire. Don’t hesitate to contact us for more information.